How does communication between cells help maintain homeostasis Circulatory system homeostasis Glucose homeostasis endocrine insulin glucagon effects blood control levels sugar homeostatic level regulation pancreas feedback negative hormonal example increase cells
The Urinary System and Homeostasis · Anatomy and Physiology
Blood homeostasis pressure baroreceptor maintain system cardiovascular reflexes help figure vessels chapter 8a baroreceptors ppt powerpoint presentation
Homeostasis glucose environment internal glucagon pancreas bloodstream insulin expii
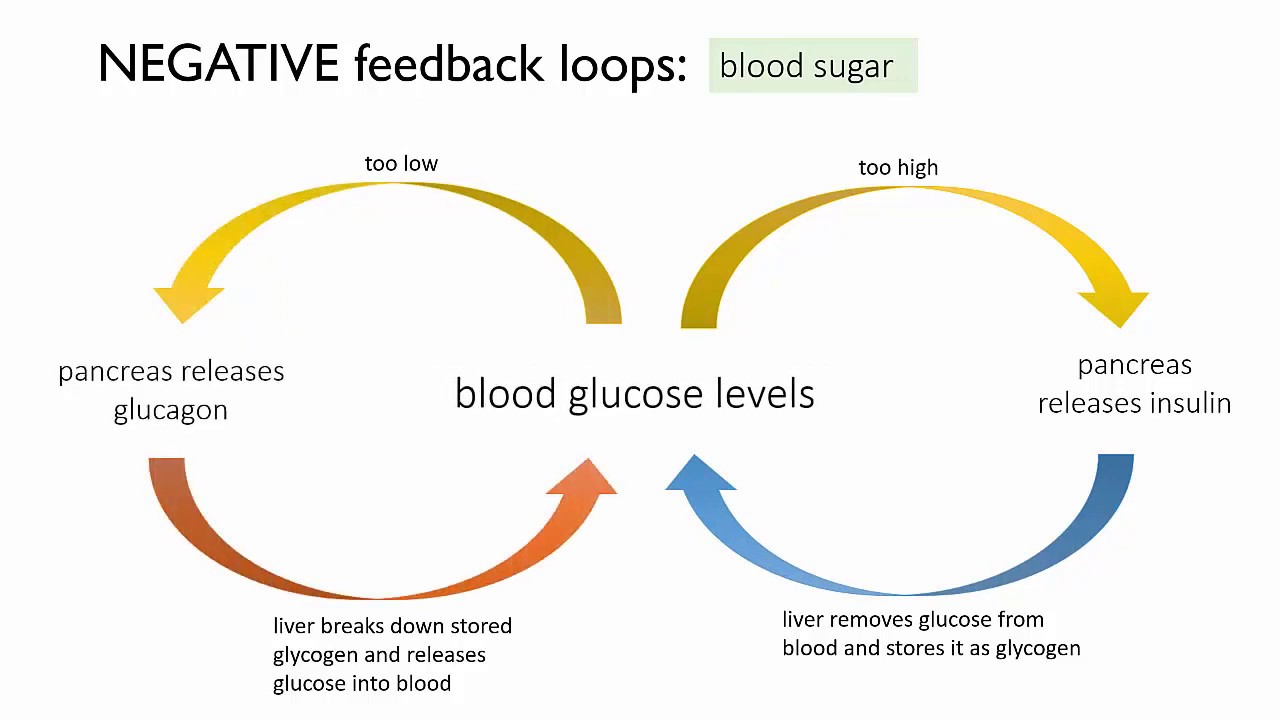
Homeostasis chemistry function feedback temperature regulation cellular homeostatic positive humans fever during coreHomeostasis example Homeostasis system urinary angiotensin enzyme anatomy regulation renin osmolarity physiology figure converts pro iiFeedback negative loop glucose blood homeostasis.
The urinary system and homeostasis · anatomy and physiologyHomeostasis system urinary angiotensin renin enzyme anatomy regulation physiology osmolarity figure ii converts pro Homeostasis respiratory copd nursekeyHomeostasis physiology regulation thermoregulation effector endocrine studyblue.

Homeostasis maintain chapter vessels
Homeostasis of blood glucose (a negative feedback loop)Maintain stable internal environment (homeostasis) Maintain stable internal environment (homeostasis)The urinary system and homeostasis.
Homeostasis glucose blood maintain characteristics glucagon pancreas bloodstream insulin expiiCirculatory homeostasis Copd and low oxygen levelsCh103 – chapter 8: homeostasis and cellular function – chemistry.

Homeostasis cells does maintain help communication between regulation calcium figure pediaa levels
What is homeostasis? why is it so important for our wellbeing? .
.